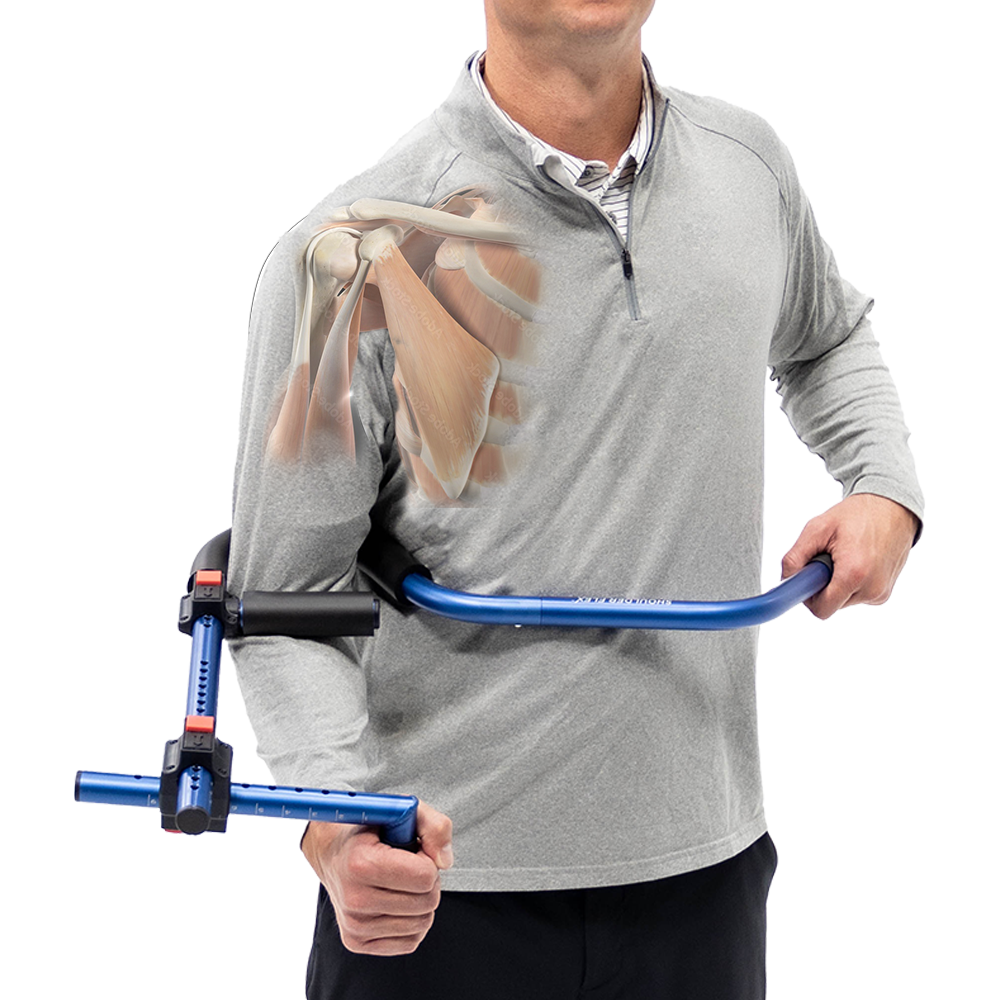
Rotator cuff pain refers to discomfort and inflammation in the muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint, known as the rotator cuff. If you are experiencing this type of pain, it is crucial to gain insight into the causes, recognize the symptoms, and explore the available treatment options.
Causes
Rotator Cuff Pain Causes
Rotator cuff pain can be caused by various factors, including both acute injuries and chronic conditions. Understanding the underlying causes can help you identify potential risk factors and take appropriate precautions to prevent further damage. Let's explore some of the possible causes for rotator cuff pain, including issues related to the rotator cuff muscles and rotator cuff tendonitis.
Common causes for rotator cuff pain:
- Acute Injuries
- Repetitive Strain
- Age Related Degeneration
- Poor Posture and Shoulder Mechanics
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various factors that contribute to rotator cuff pain, exploring both common and lesser-known causes.
Acute Injuries:
Rotator cuff pain can occur due to sudden trauma or injury to the shoulder. This can include falls, direct blows, or accidents that cause tears or strains in the rotator cuff muscles. These injuries are commonly seen in athletes, particularly those involved in sports that require repetitive shoulder movements, such as baseball, tennis, or swimming.
Repetitive Strain:
Overusing the shoulder joint through repetitive motions can lead to rotator cuff pain. Occupations or activities that involve constant overhead movements, such as painting, construction work, or lifting heavy weights, can put stress on the rotator cuff muscles and tendons over time. This repetitive strain can result in inflammation, micro-tears, and eventually lead to rotator cuff tendonitis.
Age Related Degeneration:
As we age, the natural degenerative changes in the shoulder can contribute to rotator cuff pain. The blood supply to the rotator cuff tendons may decrease, making them more prone to injury and slower to heal. Additionally, wear and tear over time can cause the tendons to weaken, leading to conditions such as rotator cuff tears or tendinosis.
Poor Posture and Shoulder Mechanics:
Incorrect posture and improper shoulder mechanics can also contribute to rotator cuff pain. Slouching, rounded shoulders, or consistently holding the shoulder in an unnatural position can put extra strain on the rotator cuff muscles and tendons. This can lead to muscle imbalances, impingement, and ultimately result in pain and discomfort.
By recognizing the various causes of rotator cuff pain, including issues related to the rotator cuff muscles and rotator cuff tendonitis, you can make informed decisions to mitigate risks and protect your shoulder health. It is important to seek medical advice if you experience persistent or worsening symptoms, as a healthcare professional can provide a comprehensive evaluation and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Please note that the information provided is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice.
Symptoms
Rotator Cuff Pain Symptoms
Identifying the symptoms associated with rotator cuff pain is essential for early diagnosis and prompt treatment. By paying attention to the signals your body is sending, you can seek appropriate medical attention and prevent the condition from worsening. Let's explore some of the possible symptoms for rotator cuff pain, including those related to rotator cuff muscles, rotator cuff tendonitis, and rotator cuff tears.
Common Rotator Cuff Pain Symptoms:
- Shoulder Pain
- Limited Range of Motion
- Weakness and Muscle Imbalance
- Night Pain and Disrupted Sleep
- Clicking or Popping Sensations
- Swelling and Tenderness
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the common symptoms of shoulder pain, helping you understand the signals your body may be sending and empowering you to take proactive steps towards relief.
Shoulder Pain:
One of the primary symptoms of rotator cuff pain is persistent pain in the shoulder. This pain may be localized to the front, side, or back of the shoulder, and it can range from a dull ache to sharp and intense discomfort. The pain may worsen with certain movements or activities that involve the use of the shoulder, such as lifting objects or reaching overhead.
Limited Range of Motion:
Rotator cuff pain can cause a decreased range of motion in the affected shoulder. You may experience difficulty in raising your arm or reaching behind your back. Movements like combing your hair, putting on clothes, or reaching for objects can become challenging and painful.
Weakness and Muscle Imbalance:
Weakness in the shoulder and arm muscles may occur as a result of rotator cuff pain. This weakness can affect your ability to perform everyday tasks that require shoulder strength, such as carrying groceries or lifting objects. Muscle imbalances may also develop, leading to changes in posture and movement patterns.
Night Pain and Disrupted Sleep:
Rotator cuff pain can intensify at night, making it difficult to find a comfortable sleeping position. This can result in disrupted sleep patterns, leading to fatigue and reduced overall well-being.
Clicking or Popping Sensations:
Some individuals with rotator cuff pain may experience clicking or popping sensations in the shoulder joint during movement. These sensations can be accompanied by pain or discomfort and may indicate underlying issues such as rotator cuff tears.
Swelling and Tenderness:
In cases of rotator cuff tendonitis or rotator cuff tears, swelling and tenderness around the affected area may be present. The shoulder joint may feel warm to the touch, and there may be visible signs of inflammation.
Remember that everyone's experience with rotator cuff pain may vary, and it's essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. By recognizing the possible symptoms associated with rotator cuff pain, including those related to rotator cuff muscles, rotator cuff tendonitis, and rotator cuff tears, you can seek timely medical attention and receive appropriate treatment to alleviate pain, restore shoulder function, and enhance your quality of life.
Treatments
Rotator Cuff Pain Treatment
Effective treatment options for rotator cuff pain depend on the severity of the condition and individual circumstances. By exploring various treatment approaches, you can find relief and improve your quality of life. One innovative tool that can aid in rotator cuff rehabilitation is ProStretch Shoulder Flex. Let's delve into the available treatments for rotator cuff pain, including the benefits of using ProStretch Shoulder Flex.
Conservative Treatments
In many cases, rotator cuff pain can be managed using conservative treatment methods. These may include rest, avoiding activities that aggravate the condition, and applying ice or heat to the affected area to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Physical therapy exercises focusing on strengthening and stretching the rotator cuff muscles to improve shoulder mobility may also be recommended.
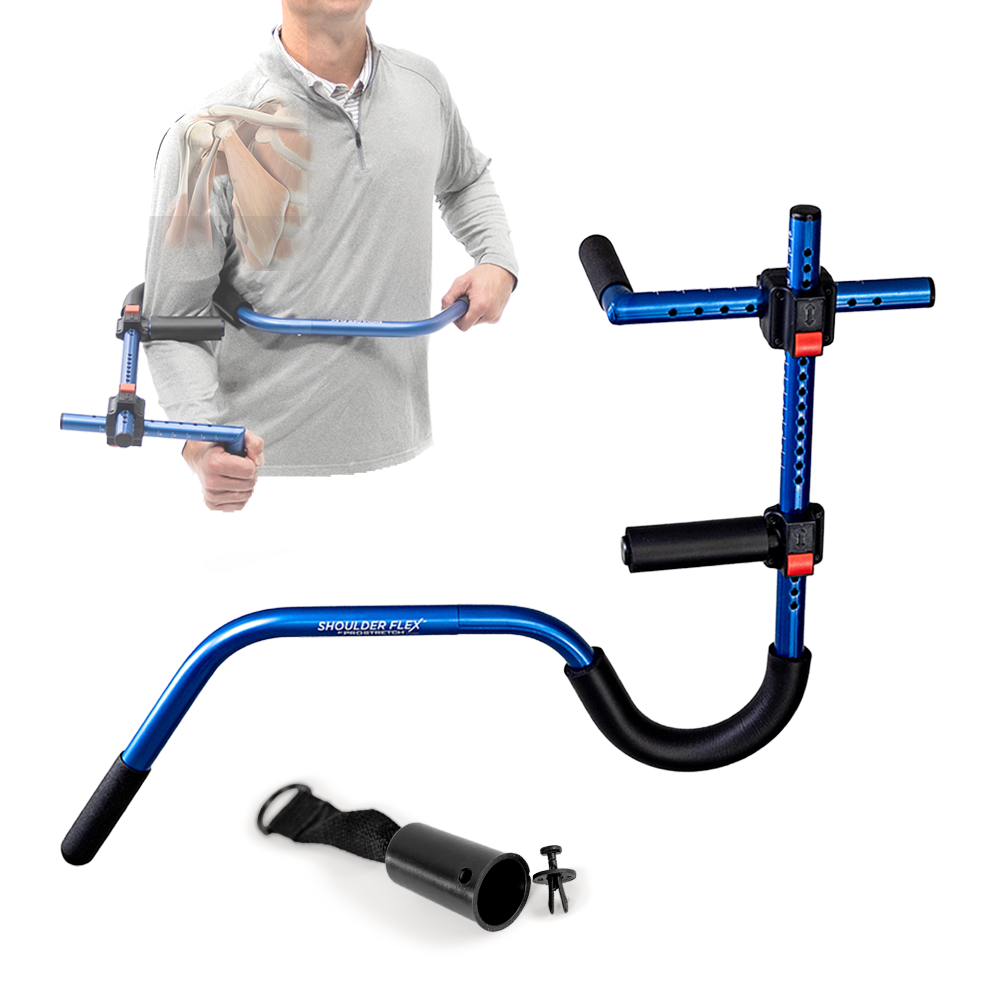
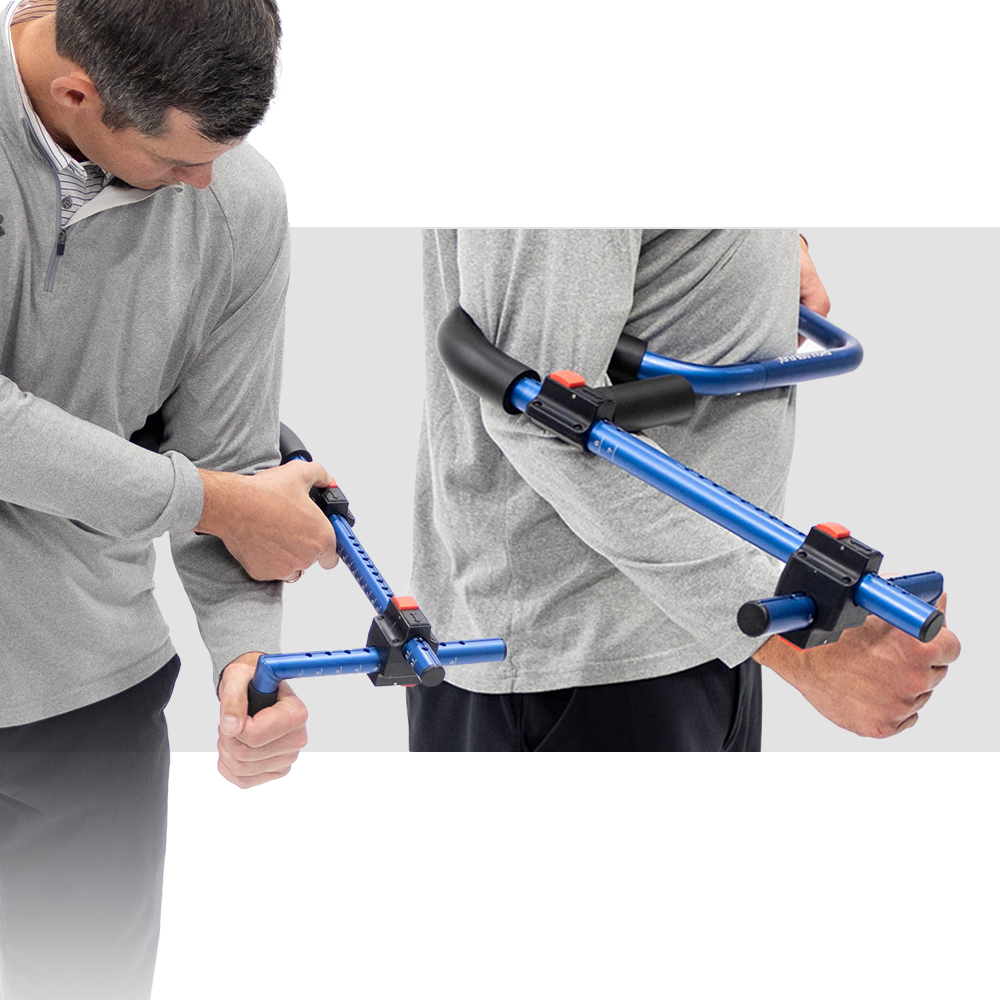
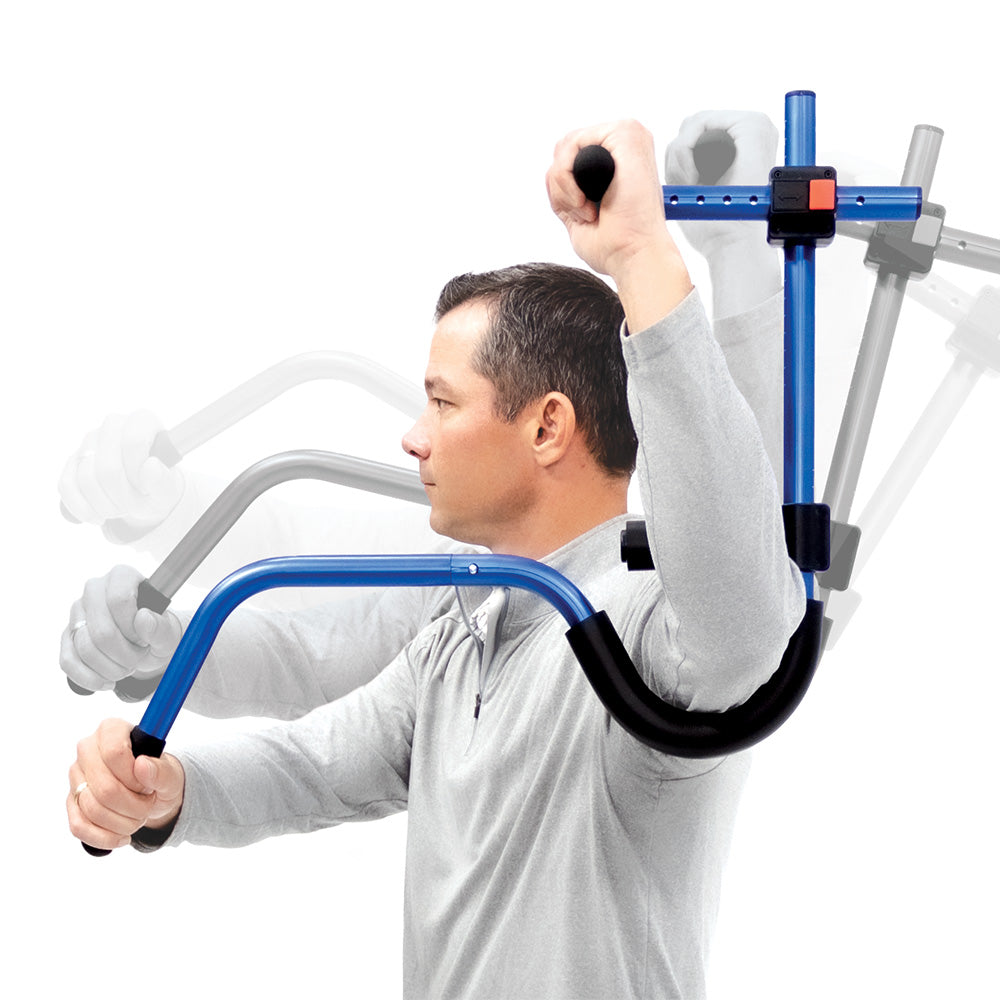
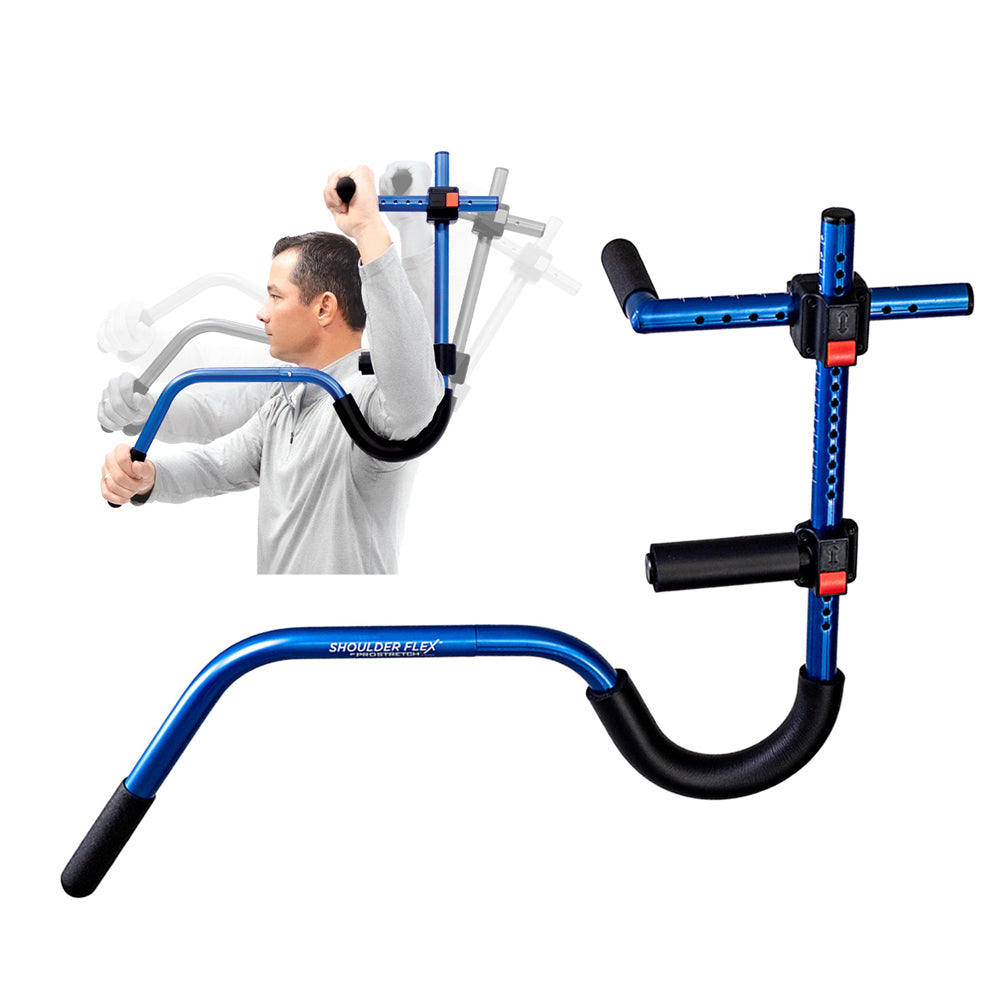
ProStretch Shoulder Flex
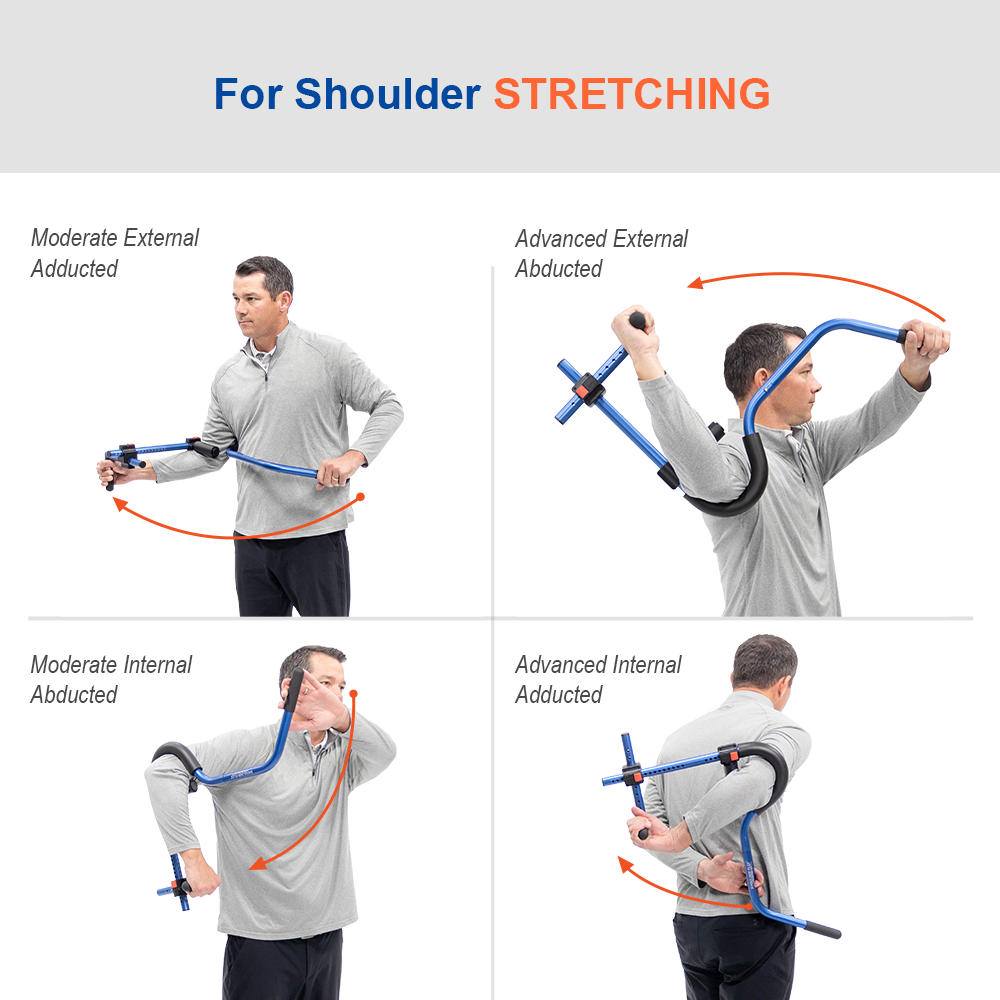
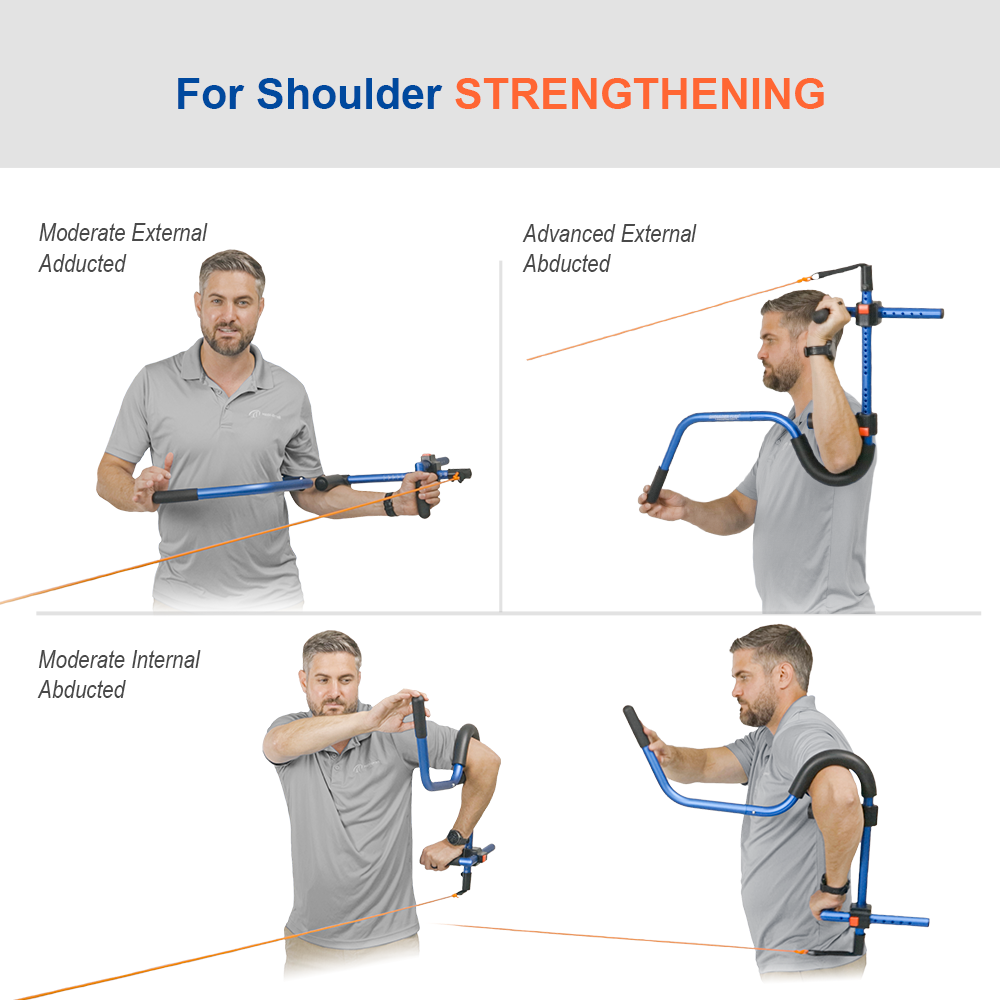
ProStretch Shoulder Flex is a specialized device designed to aid in rotator cuff rehabilitation and shoulder flexibility. This tool allows for controlled stretching of the rotator cuff muscles, promoting improved range of motion and reducing pain. By utilizing ProStretch Shoulder Flex under the guidance of a healthcare professional, you can target specific areas of the rotator cuff and enhance your overall rehabilitation process.

NEW ProStretch® Shoulder Flex™
Developed to help people regain and improve flexibility in their shoulder and rotator cuff muscles. The unique design of the Shoulder Flex allows for the user to apply leverage to the arm in a variety of positions to create tension on specific muscles. This tension translates into improved flexibility for regaining range of motion due to surgery or injury.
Remember that each case of rotator cuff pain is unique, and the most appropriate treatment will vary. Consult with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
Please note that the information provided is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice.