Jumper’s knee is an overuse injury that is common among athletes who participate in sports in which they do a lot of jumping (e.g. basketball, volleyball, long jump), but is not limited to those individuals. The term also applies to injury or inflammation where the thigh muscles tendon attach to the upper kneecap pole or where the kneecap tendon attaches to the lower leg bone. See our jumper’s knee exercises for more information.
Causes
Jumper’s Knee Pain Causes
Jumper's knee causes are believed to be due to repetitive stress placed on the patellar or quadriceps tendon during jumping. Whether you participate in jumping sports or not, you can get jumper’s knee. Risk factors include increased body weight, being bow-legged or knock-kneed, having an abnormally high kneecap or an abnormally low kneecap, and legs of unequal length. Some common jumper’s knee causes include:
- Repeated stress on the tendon that connects the kneecap to the shinbone
- Intense or frequent participation in physical activities such as jumping or running
- A sudden increase of the intensity of impact on the leg, such as during sports
- Tight muscles in the legs, as well as reduced flexibility in the thighs and hamstrings
- Imbalanced muscles, meaning that if you work out some muscles more than others, the strain on your patellar tendon could cause jumper’s knee pain
- The use of steroids often makes muscles and tendons weaker, causing jumper’s knee
- Arthritis, specifically rheumatoid, which causes inflammation of the knee joint
Symptoms
Jumper’s Knee Pain Symptoms
Jumper’s knee symptoms can include:
- Pain in the patellar tendon only after activity
- Non debilitating pain in the patellar tendon area during and after activity
- Prolonged pain in the patellar tendon area during and after activity, with increasing difficulty in being able to perform the activity
- Progressively increasing pain in the patellar tendon area that prohibits you from participating in activities
Treatments
Jumper’s Knee Pain Treatment
When looking for jumper’s knee treatment, immediate relief is what is typically sought. This often comes in the form of rest and support or compression. Jumper’s knee treatment, however, should also include stretching and strengthening exercises that will provide long term healing.
Whether you have just started to feel jumper’s knee symptoms, or you have been experiencing them for a while, the following jumper’s knee treatment options can help get you back in the game:
FOR IMMEDIATE RELIEF
Knee Support Products:
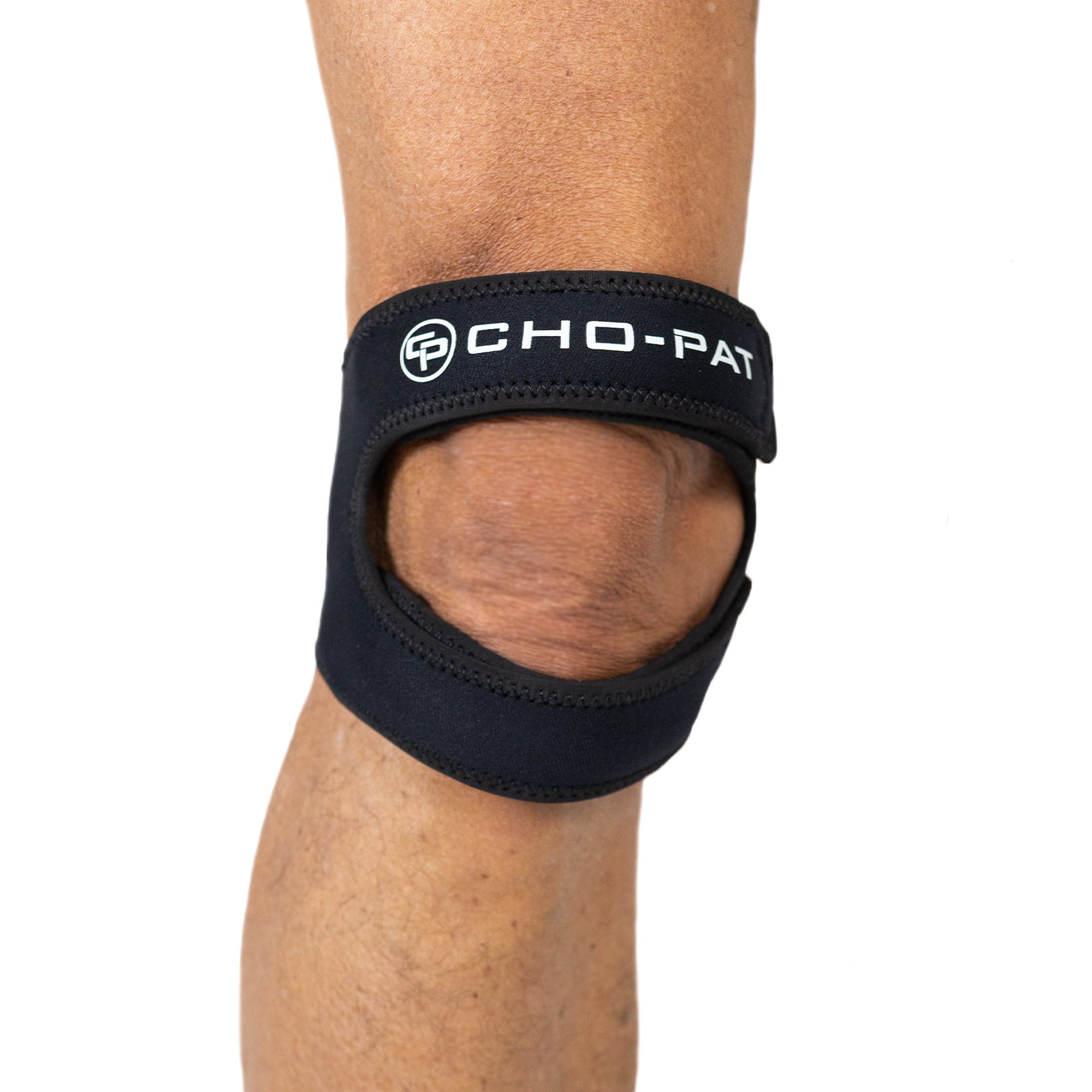
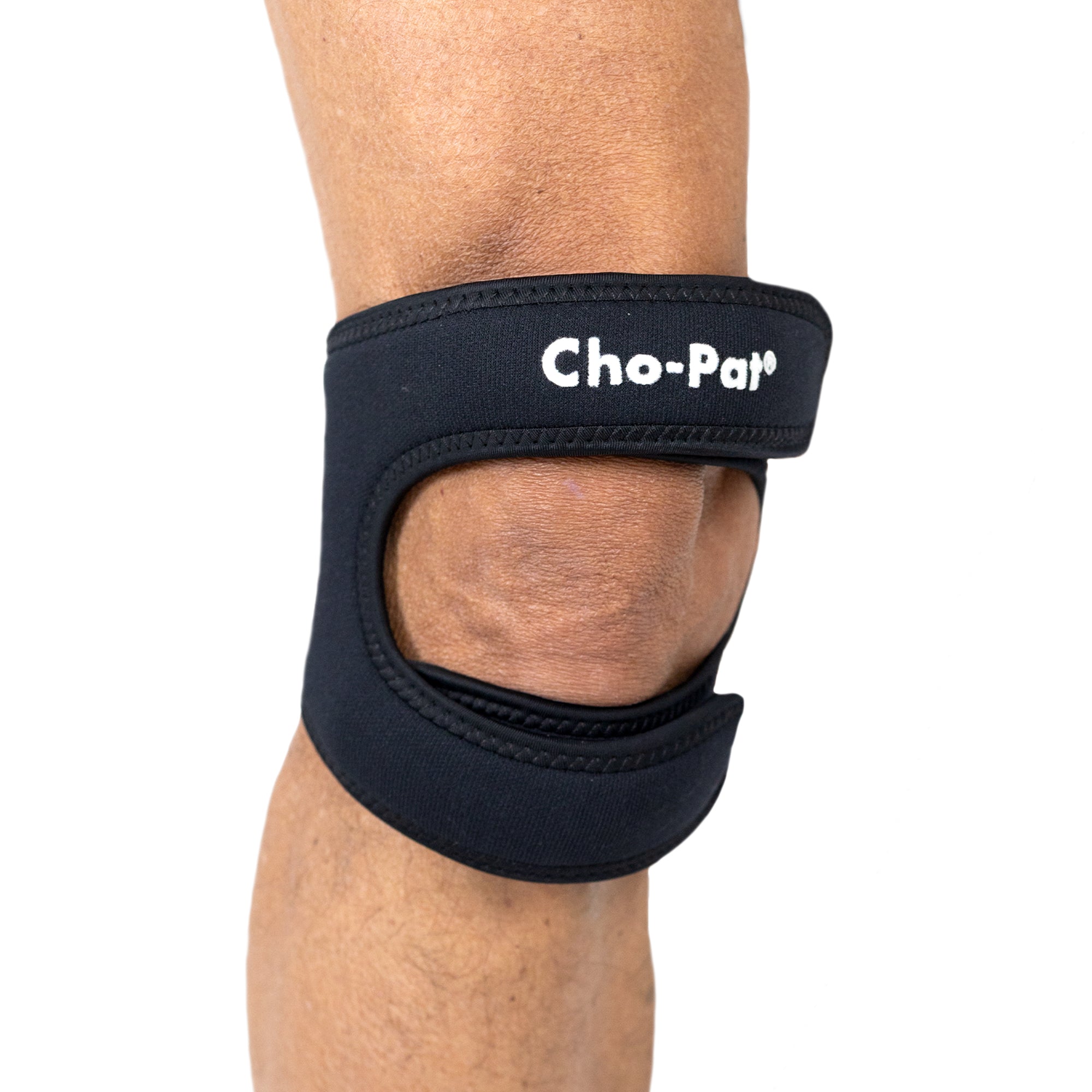
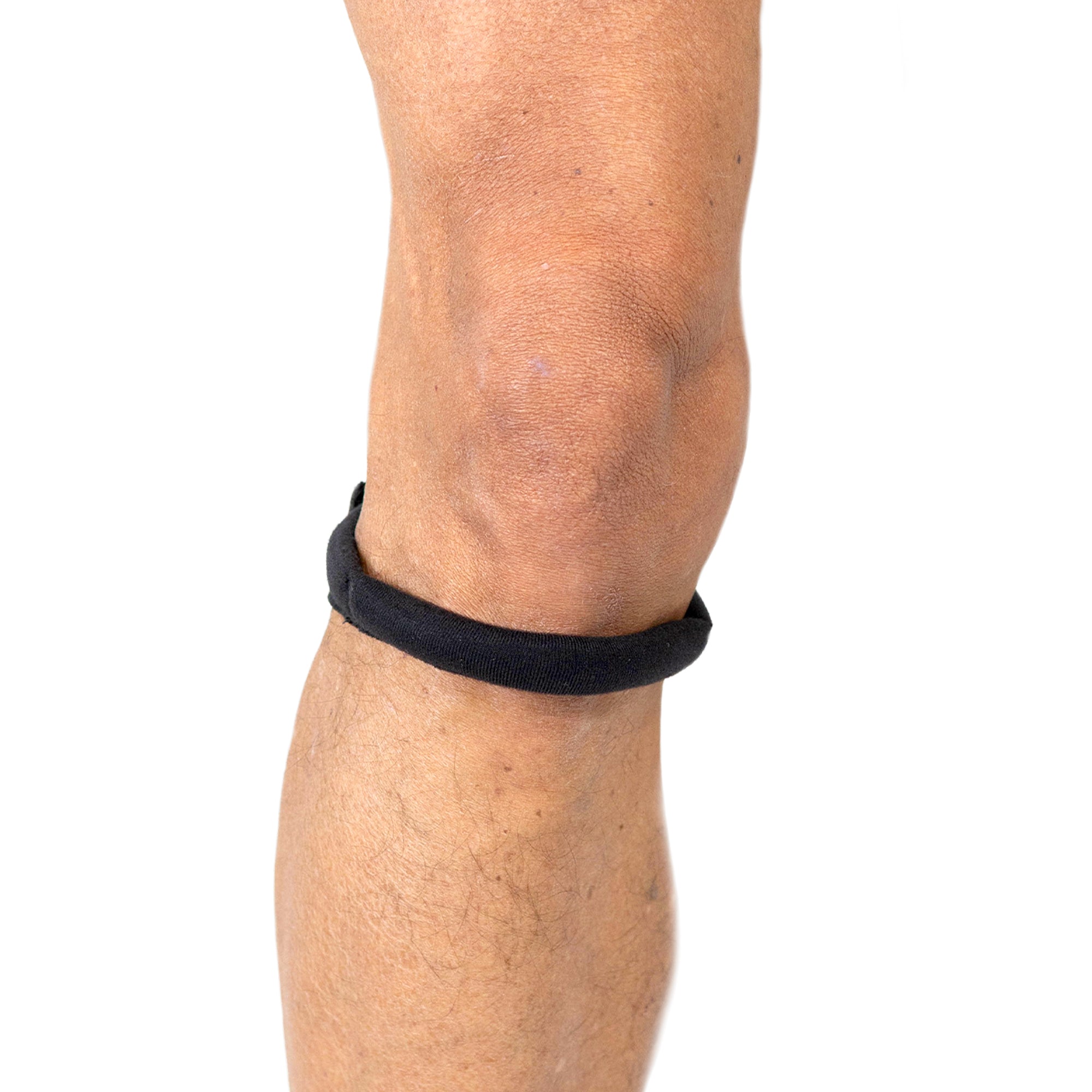
 The strap applies pressure to the patellar tendon below the kneecap as well as the tendon below the kneecap to provide strength, alignment, and stability. It also reduces the likelihood of overuse injuries. (5-Star Review) |
 Cho-Pat® Original Knee Strap ★★★★★ This provides support, mobility, and comfort to the user during activities that involve the knee. |
FOR LONG-TERM HEALING
Stretching and Strengthening Products:
|
StretchRite® Stretching Strap ★★★★★ StretchRite’s effectiveness is in the ergonomically designed handgrips that allow you to stretch comfortably, increase your range of motion in stages and visually monitor your progress. See significant improvement in flexibility and balance in just minutes a day! |
Get Quick Relief and Complete Recovery from Knee Pain
The knee is one of the most important joints in your body. If you suffer an injury or illness, the pain can be debilitating. We provide a selection of quality knee straps, patellar stabilizers, compression sleeves, and stretches to provide relief from knee pain symptoms and accelerate your recovery.
Choose from a range of the most innovative products for knee pain reduction by calling Medi-Dyne today. Contact us at 800-810-1740 or 817-251-8660.
PLEASE NOTE: The information on this website and article is for information only and should not be used as a substitute for consulting your doctor. Consult your doctor for proper diagnosis and rehabilitation.