Ankle pain is a common issue that can stem from various causes such as injuries, overuse, or underlying conditions. Whether it's a sudden sharp twinge or ongoing discomfort that affects your daily routine, addressing ankle pain early is crucial for recovery. Including targeted ankle pain exercises and stretches in your routine can help alleviate symptoms, improve flexibility, and prevent further injuries.
In this article, we'll discuss effective home stretches, how to use the ProStretch® Plus to enhance your stretching routine, and key tips for preventing both ankle and calf pain.
Table of contents:
- Ankle Pain Stretches Using ProStretch Plus
- Ankle Pain Stretching Exercises You Can Do at Home
- How to Prevent Ankle Pain?
Ankle Pain Exercises
Exercises and stretches can make a huge difference in the amount of pain you feel when you have suffered from an ankle injury. Although it may seem like an oxymoron to exercise when you’re in pain, it actually reduces the amount of pain you will feel and encourages healing, assuming you do the exercises for ankle pain properly. See our ankle pain stretches to improve range of motion. In addition to performing the ankle pain exercises properly, it is important to protect the ankles and provide them with needed support during such activities. Tuli’s® Cheetah® offer support during exercises. By wearing this product during your exercises, you will be preventing further injury to the ankles, as well as encouraging a speedier recovery process.
Ankle Pain Stretches Using ProStretch Plus
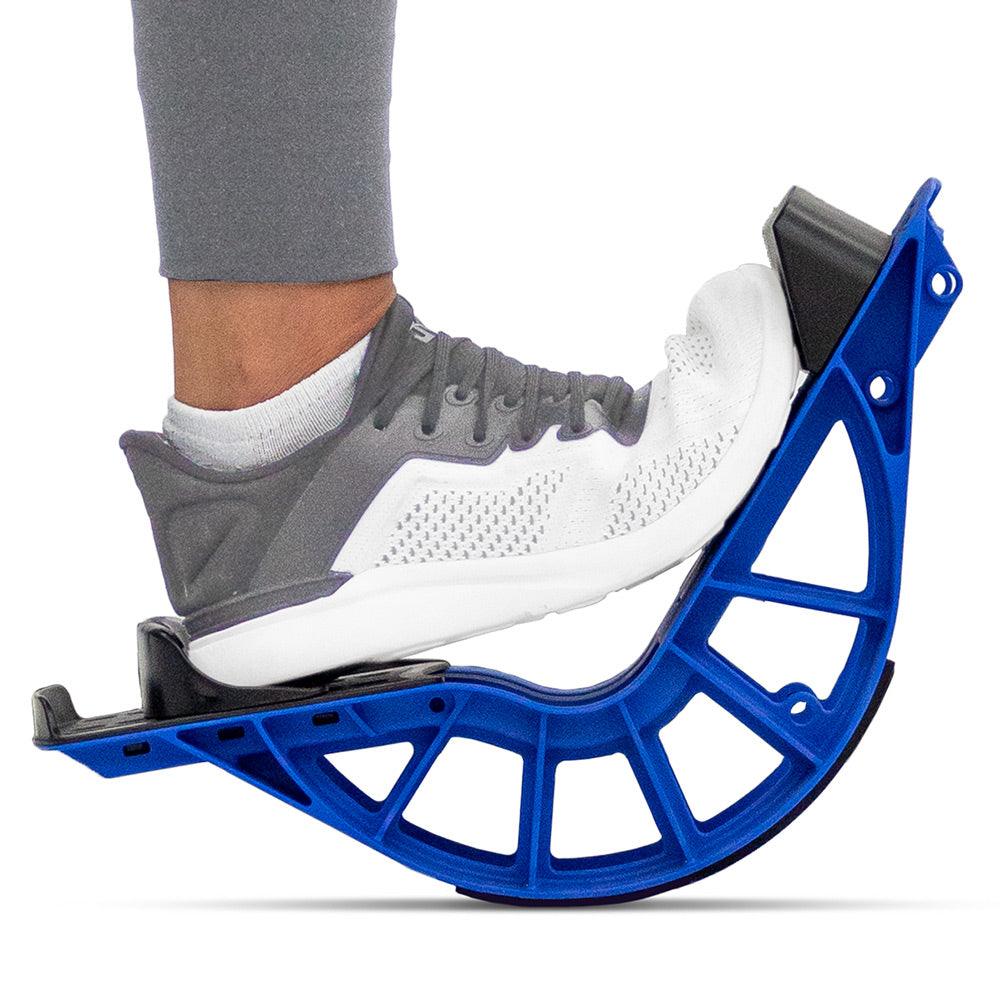
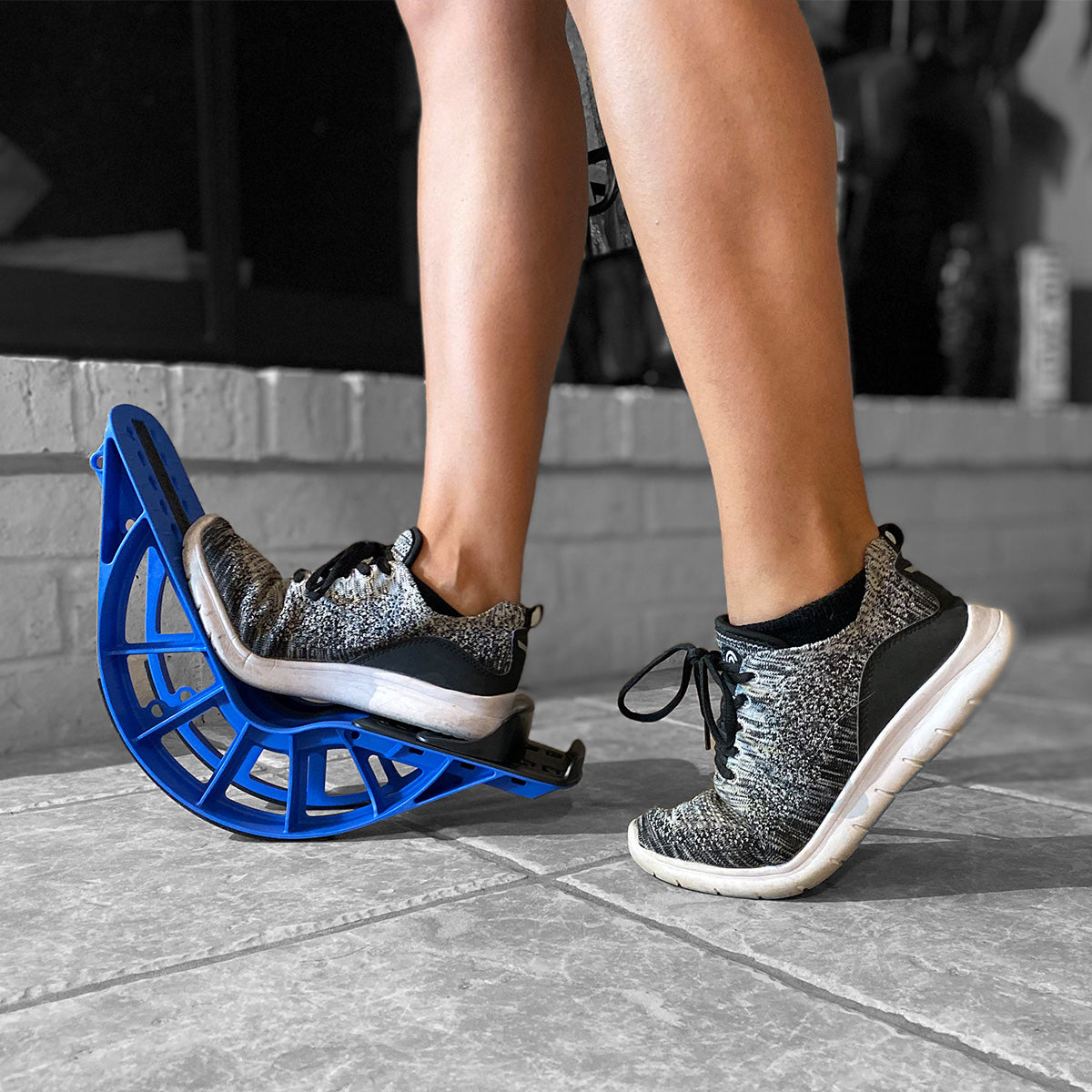
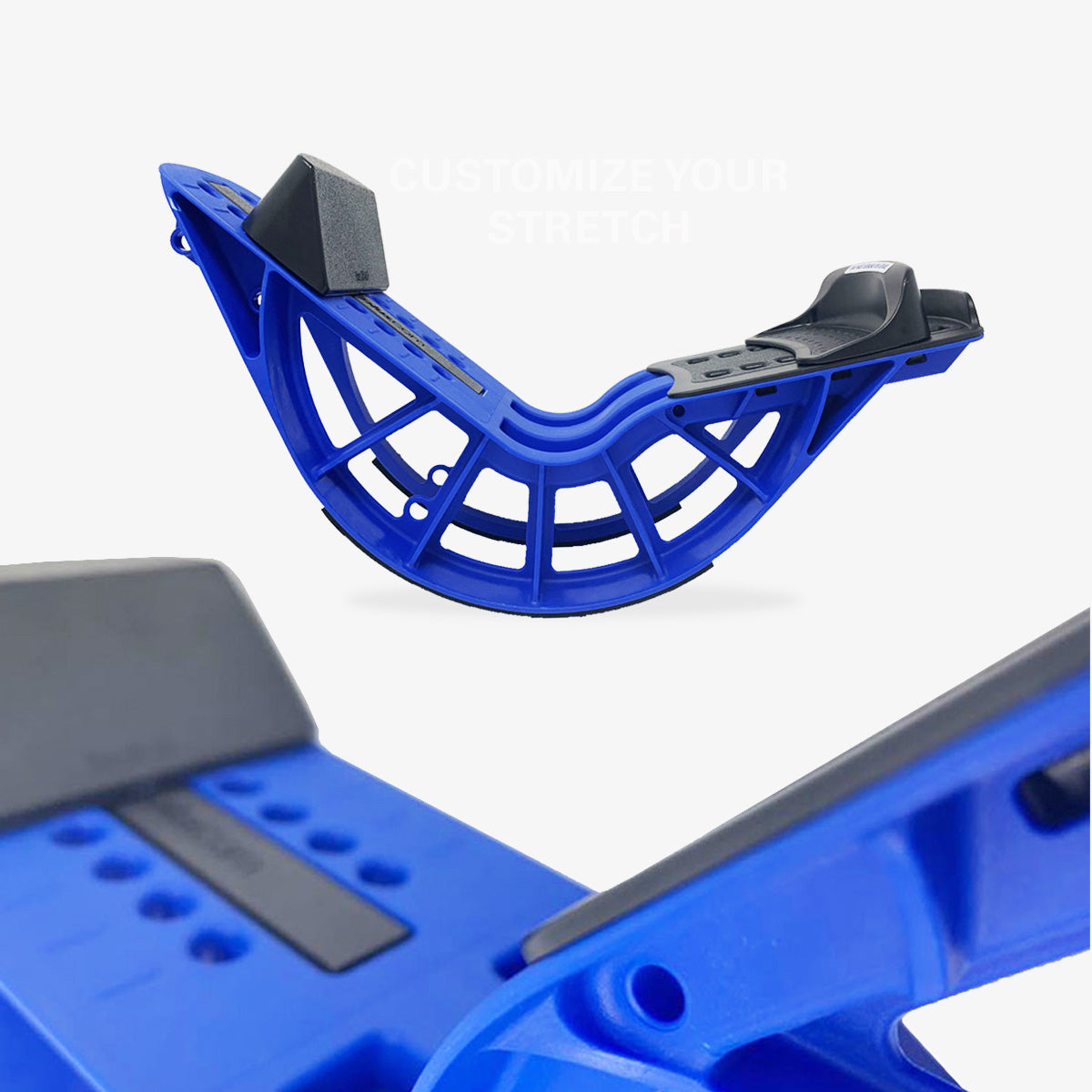
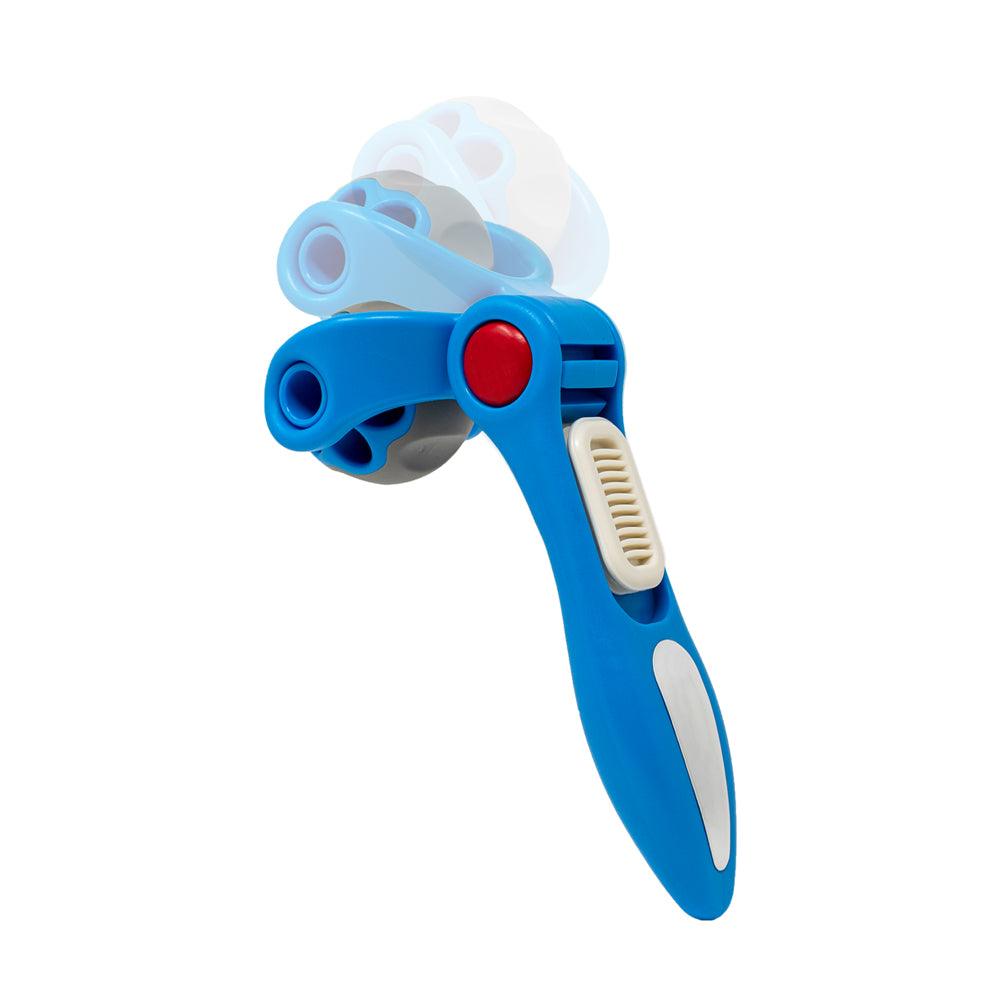
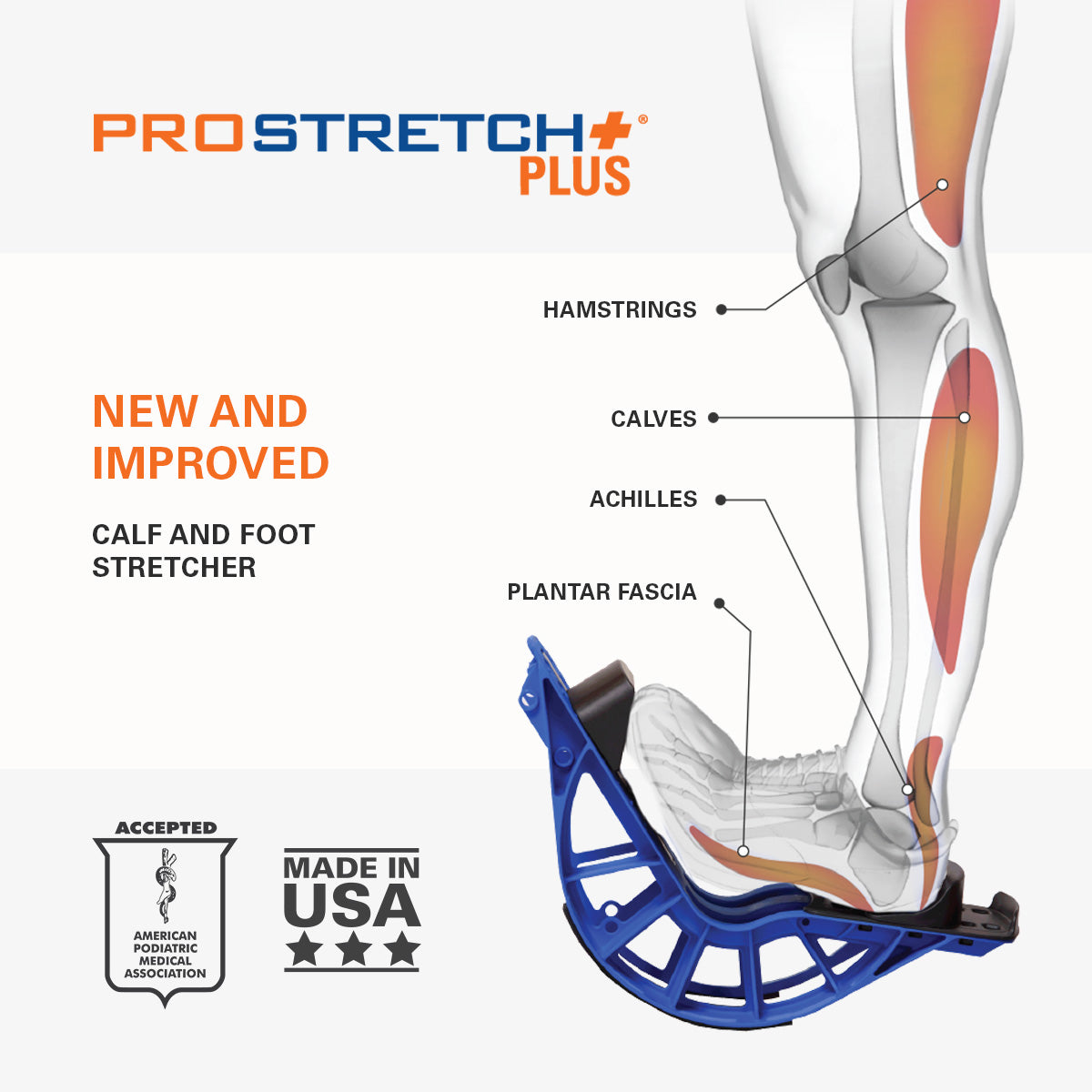
ProStretch Plus
This tool is easy to use and allows you a deep stretch into the muscles and tendons of the ankle.
- Simply stand facing a wall, resting your hands on the wall for support.
- Gently and slowly lean into the wall, while the heel in the ProStretch® Plus begins to press downward. You will feel the stretch in your calf, which will run deep into the ankle.
Plantar Flexion
- Sit on the floor with your legs extended out in front of you.
- Keep your knees locked. Moving the ankle only, point the foot forward until it begins to feel uncomfortable.
- Hold for 20 seconds, release, and repeat 10 times.
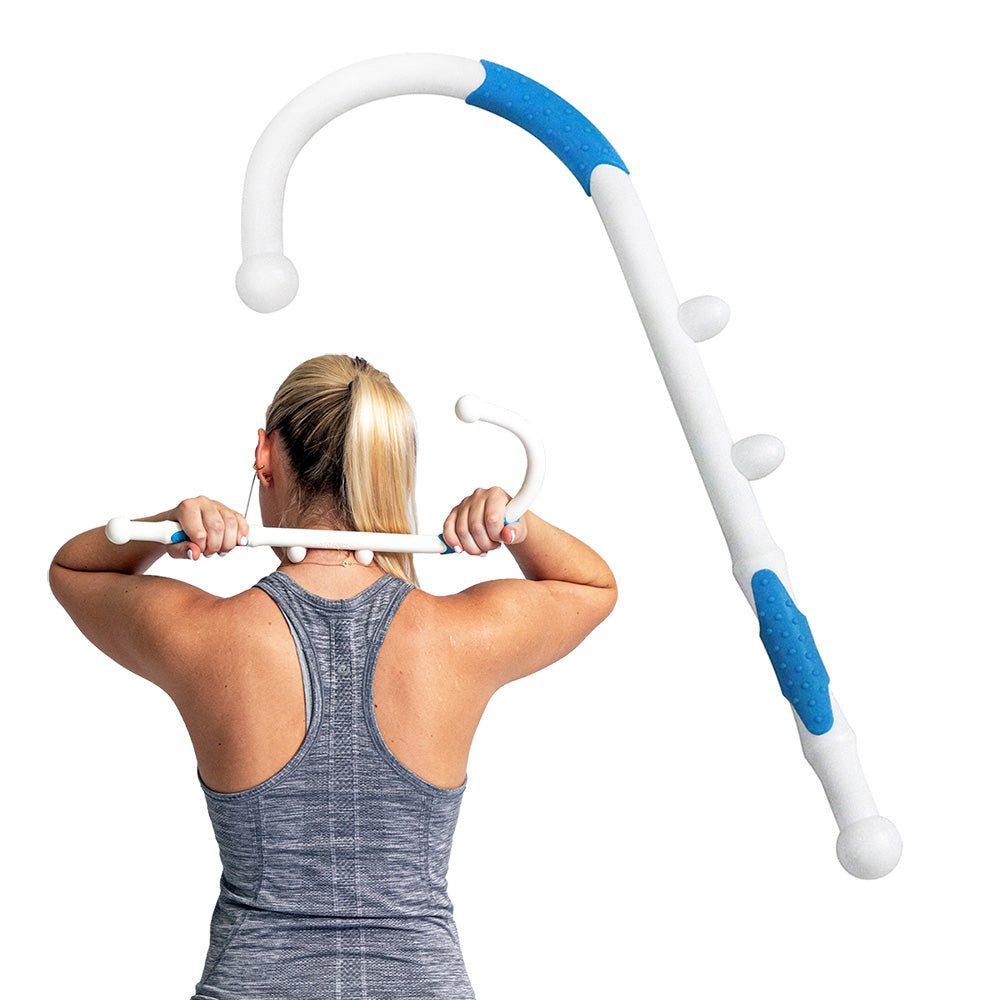
Ankle Pain Stretching Exercises You Can Do at Home
If you're experiencing ankle pain, gentle stretching exercises can help you reduce stiffness and promote healing. Here are some simple ankle pain stretches you can try at home:
Ankle Circles
- Lie down with your leg extended.
- Slowly in a circular motion rotate your ankle in one direction and then the other.
- Repeat 10 times in each direction to improve flexibility.
Calf Stretch
- Standing face a wall with your hands on the wall for support.
- Feel the calf stretch by stepping one foot back and pressing the heel into the ground while bending your front knee slightly.
- Hold this stretch for 20–30 seconds to stretch the calf and Achilles tendon, which can help relieve ankle pain.
Towel Stretch
- Sit on the floor and extend your legs in front of you.
- Loop a towel around the ball of your foot and gently pull back, feeling the stretch in your ankle and calf.
- Hold position for 20–30 seconds and repeat on the other foot.
Toe-to-Wall Stretch
- Stand facing a wall, place your toes on the wall while keeping your heel on the ground.
- Lean in slightly to stretch your ankle.
- Hold for 20–30 seconds, and repeat on both feet.
How to Prevent Ankle Pain?
Understanding how to prevent ankle pain is often the key to finding relief. The first thing to understand when learning how to prevent ankle pain is that anytime you feel pain in the ankles, you should stop what you are doing and give the ankle a rest. Rather than pushing through the pain, it is important that you take time to apply ice, reduce inflammation, and allow the ankle a break from the workout.
Prevention is key when it comes to avoiding ankle and calf pain. Here are a few tips to keep your ankles strong and pain-free:
- Warm-Up - Always warm up before engaging in physical activity to increase blood flow to your muscles and joints. This can help prevent sudden injuries that lead to ankle pain.
- Strengthening Exercises - Incorporate strengthening exercises into your routine, such as calf raises and balance exercises, to build stability in your ankles and calves.
- Wear Proper Footwear - Wearing supportive shoes can help reduce strain on your ankles. Make sure your shoes provide adequate cushioning and stability for your activities.
- Stretch Regularly - Consistently performing ankle pain stretches, especially after exercise, can help maintain flexibility and prevent stiffness.
- Listen to Your Body - Avoid pushing through pain. If you experience discomfort, take a break and give your ankle time to rest and recover.
Conclusion
By incorporating these ankle pain exercises and stretches into your routine, you can help alleviate pain, improve mobility, and prevent future injuries.
PLEASE NOTE: The information on this website and article is for information only and should not be used as a substitute for consulting your doctor. Consult your doctor for proper diagnosis and rehabilitation.