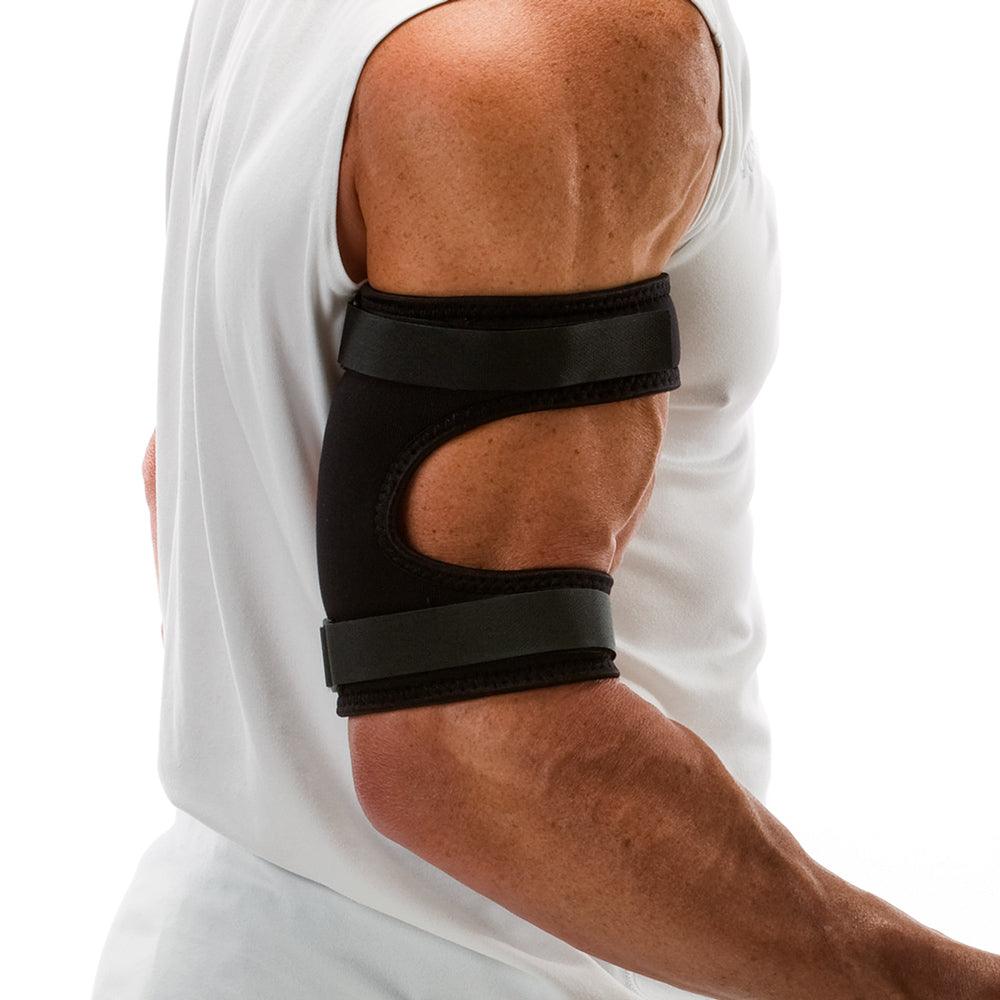
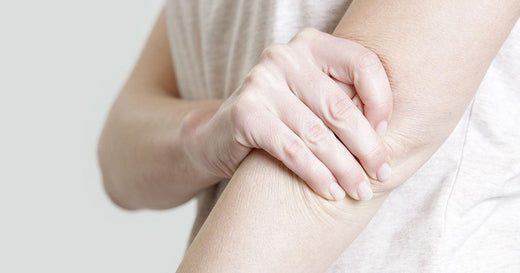
Dealing with the discomfort of swimmer’s elbow can be discouraging, making the prospect of engaging in exercises seem daunting. However, maintaining a certain level of activity is important to prevent the condition from worsening and to target the muscles contributing to the problem. Despite the challenges, there are safe swimmer's elbow stretches and exercises designed to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and facilitate a return to your regular activities.
What is Swimmer's Elbow Tendonitis?
Swimmer's elbow, also known as medial epicondylitis or swimmer's elbow tendonitis, is a condition that consists of an inflammation and pain on the inner side of the elbow. Mainly impacting the tendons linking the muscles of the forearm, also known as the medial epicondyle, which is the bony protrusion located in the inner side of the elbow.
While the name suggests a strong association with swimming, this condition is not exclusive to swimmers and can affect individuals engaged in various repetitive arm motions. The repetitive nature of swimming strokes, particularly the forceful and continuous use of the forearm muscles during activities like the freestyle stroke, can lead to microtears and inflammation in the tendons, resulting in the characteristic pain and discomfort associated with swimmer's elbow tendonitis.
Symptoms often include pain, tenderness, and swelling on the inner side of the elbow, making it essential for affected individuals to seek appropriate medical attention and adopt targeted exercises and treatments to alleviate discomfort and prevent further injury.
Swimmer's Elbow Stretches
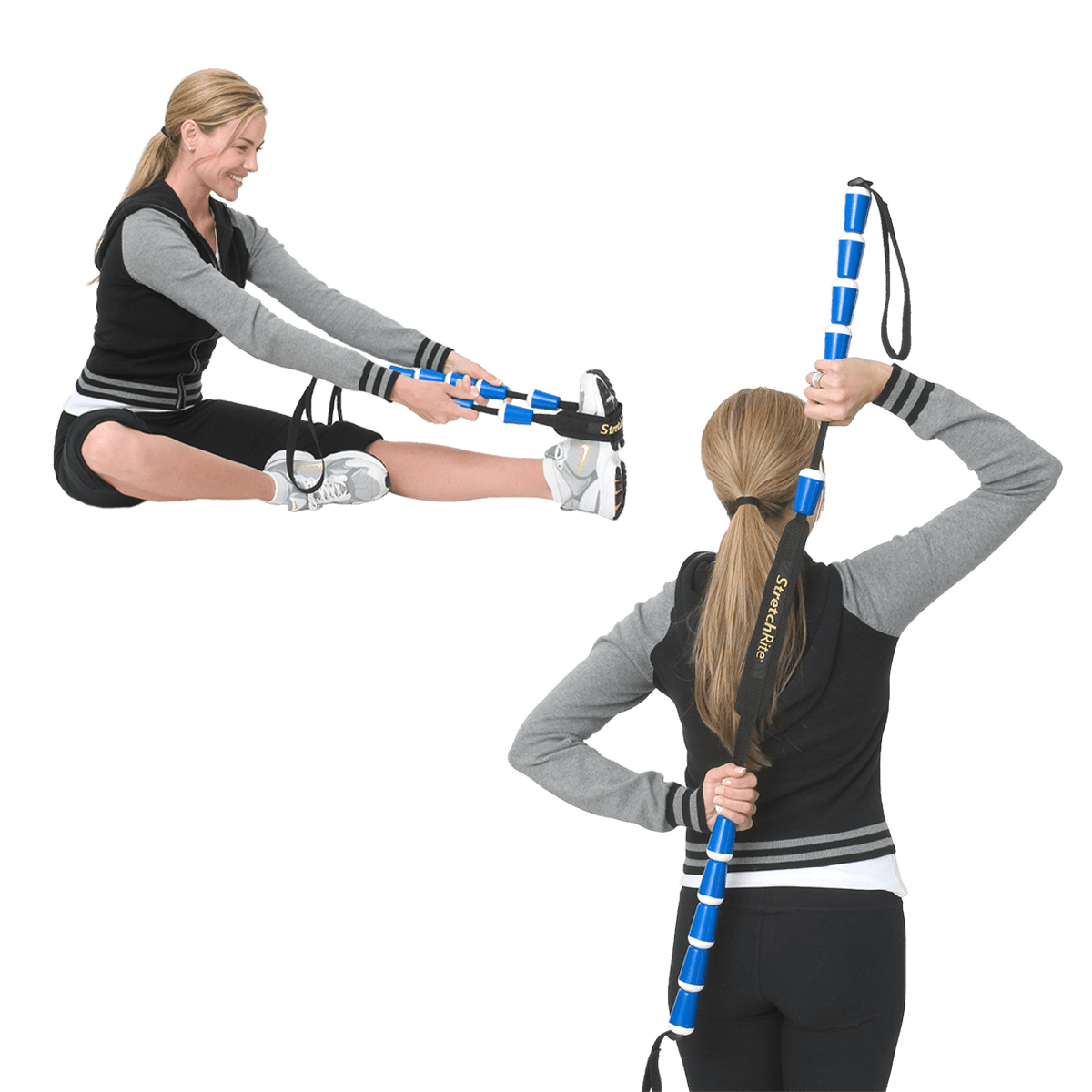
Swimmers, from amateurs to collegiate and professional athletes, are no strangers to the demanding nature of their sport. However, with the constant repetition of strokes, swimmers are prone to overuse injuries, including the notorious swimmer's elbow. This condition, also known as medial epicondylitis, can cause discomfort and affect performance. In this article, we'll explore a series of effective stretching strap exercises designed to alleviate swimmer's elbow pain, catering to individuals at various skill levels.
These exercises utilize the ProStretch® StretchRite® Stretching Strap, a static stretching strap designed with ergonomically shaped handles to ensure a secure grip and facilitate deeper stretching. However, alternatives such as a Yoga strap, a non-elastic exercise band, or a similar tool can also be used.
Hamstring Stretch with Modified Grip
- Take a seat on the ground with your legs stretched out in front of you.
- Loop the stretching strap around your toes, holding one end in each hand.
- Maintain your back straight and gently lean forward, targeting your hamstrings. This stretch indirectly helps reduce tension in the shoulders and elbows.
Quad Stretch for Recovery
- Lie on your stomach and loop the strap around your ankle.
- Gradually pull the strap to bring your heel towards your glutes, emphasizing the quadriceps. This stretch aids in overall recovery and flexibility for swimmers.
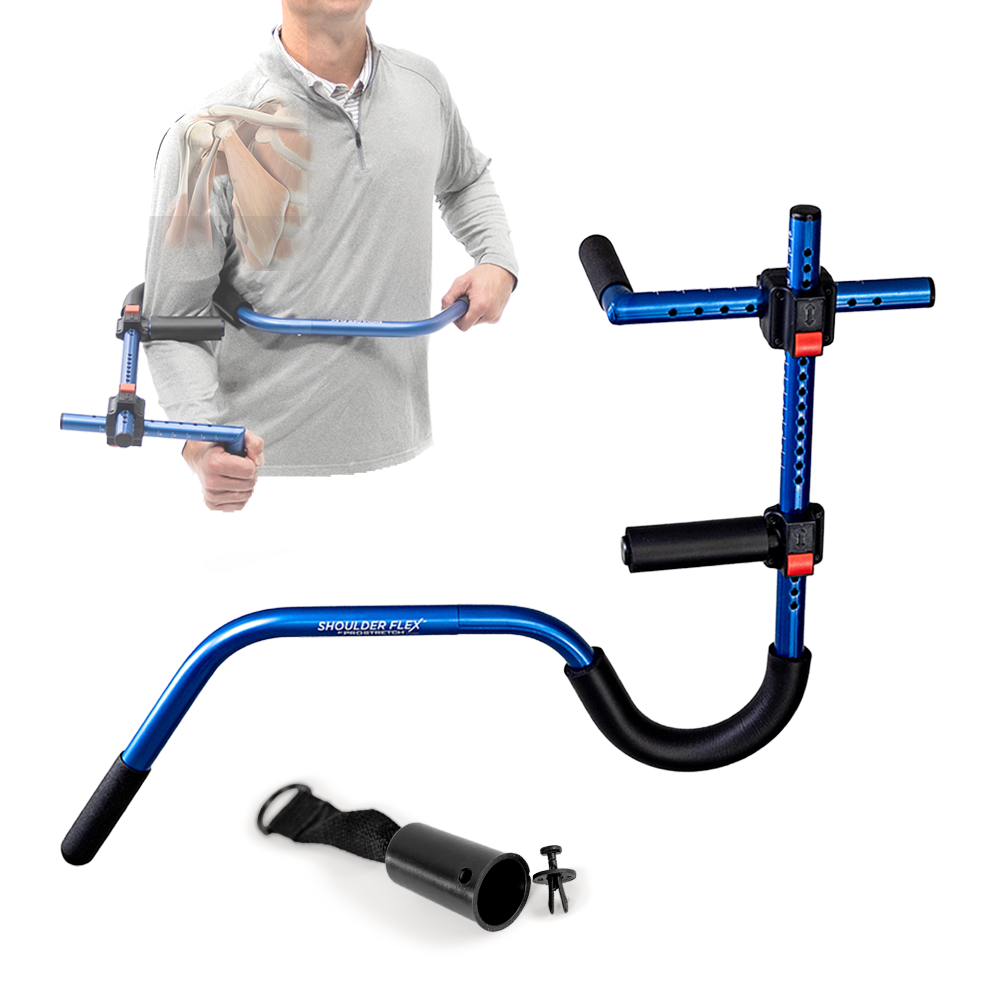
Dynamic Shoulder Opener
- Hold the strap with both hands, arms extended straight out in front of you.
- Lift the strap overhead and then lower it behind your head, creating a dynamic shoulder stretch.
- This exercise helps improve shoulder mobility and flexibility, essential for a smooth swim stroke.
Chest Expansion for Improved Posture
- Hold the strap with both hands behind your back, arms straight. Open your chest by lifting the strap, promoting better posture and relieving stress on the elbows.
- This stretch is particularly beneficial for swimmers who spend extended periods in the water.
Seated Forward Bend for Flexibility
- Sit and with your legs extended loop the strap around your feet.
- Hold the strap and gently lean forward, stretching the hamstrings and lower back, indirectly addressing elbow pain.
Hip Mobility for Better Turns
- Lie on your back on the floor and loop the strap around the ball of your left or right foot.
- Straighten the leg while holding the strap, enhancing hip mobility crucial for effective turns in the water.
Lateral Leg Stretch for Core Engagement
- Sit with legs wide apart and grasp the strap with both hands.
- Lean to one side, using the strap to deepen the stretch and engage the core muscles. This exercise aids in overall flexibility and core stability, contributing to a more efficient swim.
Triceps Stretch for Arm Recovery
- Hold one end of the strap and reach it down your back.
- Use the opposite hand to grab the other end behind your back, targeting the triceps. This stretch is vital for relieving tension in the arms and promoting faster recovery.
Wrist Flexor Stretch
- Loop the strap around your fingers and gently pull back, targeting the wrist flexors.
- This stretch is particularly useful for addressing the finer muscles in the forearm, crucial for a powerful swim stroke.
Calf Stretch for Overall Leg Relief
- Sit with legs extended and loop the strap around the ball of one foot.
- Gently pull the strap towards you, relieving tension in the calves, indirectly aiding in elbow pain relief.
Conclusion
Swimmer's elbow is a challenge faced by athletes at all levels, but with targeted stretching strap exercises, swimmers can actively contribute to their recovery and injury prevention. Regardless of whether you're an amateur, collegiate, or professional swimmer, incorporating these exercises into your routine can enhance flexibility, alleviate swimmer's elbow pain, and contribute to overall performance in the pool.
As with any exercise routine, it's essential to listen to your body, and if persistent pain persists, consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice. Dive into these stretching strap exercises, and swim with strength and comfort.
PLEASE NOTE: The information on this website and article is for information only and should not be used as a substitute for consulting your doctor. Consult your doctor for proper diagnosis and rehabilitation.